IBM Data Course 3: DS Methodology
Posted on 03/04/2019, in Data Science.This note was first taken when I learnt the IBM Data Professional Certificate course on Coursera.
settings_backup_restore
Go back to Course 1 & 2.
keyboard_arrow_right
Go to Course 4.
tocIn this post
cloud_download
See white paper about Methodology.
Week 1: From Problem to Approach
- Data Science Methodology aims to answer the following 10 questions in this prescribed sequence:
- From the problem to approach:
- What is the problem that you are trying to solve?
- How can you use data to answer the question?
- Working with the data:
- What data do you need to answer the question?
- Where is the data coming from (identify all sources) and how will you get it?
- Is the data that you collected representative of the problem to be solved?
- What additional work is required to manipulare and work with the data?
- Deriving the answer:
- In what way can the data be visualized to get to the answer that is required?
- Does the model used really answer the initial question or does it need to be adjusted?
- Can you put the model into practice?
- From the problem to approach:
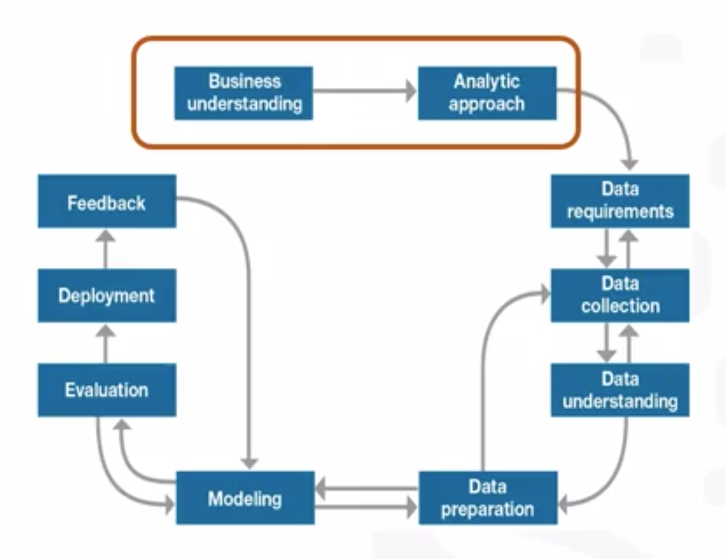
Business Understanding
- If you have a deadline and a problem need to be solved. You met your boss and both of you have discussed about the track you need to keep to solve this problem. You feel that everything will be ok until you step you first steps into the solving. You realize that there are some more additional problems need to be clear but your boss is not there for your extend discussion. What will you do? Keep forward or stop and clarification? Data Science Methodology begins with spending the time to seek clarification.
- Clarifying the problem helps you choose the right data to be used to answer the question.
- Establishing a clearly defined question starts with understanding the GOAL of the person who is asking the question.
- Goal > Objectives supporting the goals
- Case study
- In the case study, the question being asked is: What is the best way to allocate the limited healthcare budget to maximize its use in providing quality care?
- Goals: to provide quality care without increasing costs.
- Objectives: to review the process to identify inefficiencies.
- Decision-tree model (wiki).
- Decision trees are built using recursive partitioning to classify the data.
- When partitioning the data, decision trees use the most predictive feature (ingredient in this case) to split the data.
- Predictiveness is based on decrease in entropy - gain in information, or impurity.
- A tree stop growing at a node when
- Pure or nearly pure.
- No remaining variables on which to further subset the data.
- The tree has grown to a preselected size limit.
- Steps:
- Predict CHF readmission outcome (Y or N) for each patient
- Predict the readmission risk for each patient
- Understand explicitly what combination of events lead to the predicted outcome for each patient
- Easy to understand and apply to new patients to predict their readmission risk
Analytic Approach
- Once a strong understanding of the question is established, the analytic approach can be selected.
- This means identifying what type of patterns will be needed to address the question most effectively.
- Types of questions?
- If the question is to determine probabilities of an action: use a predictive model
- If the question is to show relationships: use a descriptive model
- If the question requires a yes/no answer: use a classification model
Lab: understanding problem to approach
keyboard_arrow_right
Go to see the notebook.
Week 1: from Requirements to Collection
Data Requirements
- So, if the problem that needs to be resolved is the recipe, so to speak, and data is an ingredient, then the data scientist needs to identify: which ingredients are required, how to source or the collect them, how to understand or work with them, and how to prepare the data to meet the desired outcome.
- The chosen analytic approach determines the data requirements. Specifically, the analytic methods to be used require certain data content, formats and representations, guided by domain knowledge.
Data Collection
- After the initial data collection is performed, an assessment by the data scientist takes place to determine whether or not they have what they need. As is the case when shopping for ingredients to make a meal, some ingredients might be out of season and more difficult to obtain or cost more than initially thought.
- In the initial data collection stage, data scientists identify and gather the available data resources. These can be in the form of structured, unstructured, and even semi-structured data relevant to the problem domain.
Lab: understanding requirement to collection
keyboard_arrow_right
Go to see the notebook.
Week 2: from understanding to preparation
- Data understanding: what does it mean to “prepare” or “clean” data?
- Data preparation: what are ways in which data is prepared?
Data understanding
- The data understanding phase of CRISP-DM involves taking a closer look at the data available for mining. This step is critical in avoiding unexpected problems during the next phase–data preparation–which is typically the longest part of a project.
- Data understanding involves accessing the data and exploring it using tables and graphics that can be organized in IBM® SPSS® Modeler using the CRISP-DM project tool. This enables you to determine the quality of the data and describe the results of these steps in the project documentation.
- Descriptive statistics: univariate statistics, pairwise statistics, histogram.
- Data quality: missing values, ivalid or misleading values.
- Iterative data collection and data understanding
- It was working through the Data Understanding staging that the initial definition was found to be incomplete.
Data preparation (concepts)
- Look like remove dust from the fruit in washing.
- Data Preparation is the process of collecting, cleaning, and consolidating data into one file or data table, primarily for use in analysis.
- Whether or not database-native algorithms are used, data preparations should be pushed back to the database whenever possible in order to improve performance.
- The most consuming face of a data science project. (70-90% project's time)
- Data understanding to preparation: make data to be easier to work with.
- Feature engineering:
- It is the process of using domain knowledge of the data to create features that make the machine learning algorithms work.
- Feature engineering is critical when machine learning tools are being applied to analyze the data.
- The text analysis is critical to ensure that the proper groupings are set, and that the programming is not overlooking what is hidden within.
- The data preparation phase sets the stage for the next steps in addressing the question.
- Data Understanding stage is the stage that encompasses all activities related to constructing the dataset.
- Select the correct statement about what data scientists and database administrators (DBAs) do during the Data Preparation stage.
- During the Data Preparation stage, data scientists and DBAs define the variables to be used in the model.
- During the Data Preparation stage, data scientists and DBAs determine the timing of events.
- During the Data Preparation stage, data scientists and DBAs aggregate the data and merge them from different sources.
- During the Data Preparation stage, data scientists and DBAs identify missing data.
- It is vital to take your time in this area, and use the tools available to automate common steps to accelerate data preparation.
- Data scientists and DBAs aggregate the data themselves and merge them from different sources, not the clients or stakeholders.
From modeling to evaluation
Modeling Concepts
- Modelling is the stage in the data science methodology where the data scientist has the chance to sample the sauce and determine if it’s bang on or in need of more seasoning.
- 2 main questions:
- purpose of data modeling?
- characteristics of this process?
- Focus on developing models that are either descriptive or predictive.
- Use training / test sets
- training set : a set of historical data in which the outcomes are already known.
- In John Rollins’ descriptive Data Science Methodology, the framework is geared to do 3 things:
- First, understand the question at hand.
- Second, select an analytic approach or method to solve the problem,
- and third, obtain, understand, prepare, and model the data.
Modeling - Case study
- Modeling: in what way can the data be visualized to get the answer that is required?
- False positive (Type I error): A false positive is where you receive a positive result for a test, when you should have received a negative results. It’s sometimes called a “false alarm” or “false positive error.” (source)
- A pregnancy test is positive, when in fact you aren’t pregnant.
- A cancer screening test comes back positive, but you don’t have the disease.
- A prenatal test comes back positive for Down’s Syndrome, when your fetus does not have the disorder(1).
- Virus software on your computer incorrectly identifies a harmless program as a malicious one.
- False positives can be worrisome, especially when it comes to medical tests
- A related concept is a false negative (Type II error), where you receive a negative result when you should have received a positive one. For example, a pregnancy test may come back negative even though you are in fact pregnant.
Evaluation
- Evaluation: Does the model used really answer the initial question or does it need to be adjusted?
- The modeling and evaluation stages are done iteratively.
- Model evaluation is performed during model development and before the model is deployed.
- Evaluation allows the quality of the model to be assessed but it’s also an opportunity to see if it meets the initial request.
- Evaluation answers the question: Does the model used really answer the initial question or does it need to be adjusted?
- 2 main phases
- Diagnostic measures: used to ensure the model is working
- If the model is a predictive model, a decision tree can be used to evaluate if the answer the model can output, is aligned to the initial design. It can be used to see where there are areas that require adjustments.
- If the model is a descriptive model, one in which relationships are being assessed, then a testing set with known outcomes can be applied, and the model can be refined as needed.
- Statistical signigicance: This type of evaluation can be applied to the model to ensure that the data is being properly handled and interpreted within the model.
- Diagnostic measures: used to ensure the model is working
- Model Evaluation includes ensuring the model is designed as intended.
- ROC curve: ROC stands for receiver operating characteristic curve. ROC curve is a useful diagnostic tool in determining the optimal classification model.
From Deployment to Feedback
Deployment
- Once a satisfactory model has been developed and is approved by the business sponsors, it is deployed into the production environment or a comparable test environment.
- While a data science model will provide an answer, the key to making the answer relevant and useful to address the initial question, involves getting the stakeholders familiar with the tool produced.
- In this scenario, the business people translated the model results so that the clinical staff could understand how to identify high-risk patients and design suitable intervention actions. The goal, of course, was to reduce the likelihood that these patients would be readmitted within 30 days after discharge.
Feedback
- Once in play, feedback from the users will help to refine the model and assess it for performance and impact.
- The data science methodology is highly iterative, ensuring the refinement at each stage in the game.
- Analyzing this feedback enables data scientists to refine the model to improve its accuracy and usefulness. They can automate some or all of the feedback-gathering and model assessment, refinement and redeployment steps to speed up the process of model refreshing for better outcomes.
