IBM Data Course 5: Databases and SQL for DS (w3-w4)
Posted on 08/04/2019, in Data Science, Python.This note was first taken when I learnt the IBM Data Professional Certificate course on Coursera.
Week 3: Accessing Databases using Python
Accessing databases using Python
- Python supports relational database systems.
- Notebook interfaces: matlab notebook, maple worksheet, IPython Jupyter notebook, R Markdown, Apache Zepplin, Apache Spark notebook and Databricks cloud.
- Jupyter notebook supports 40 languages: python, R, Julia, Scala.
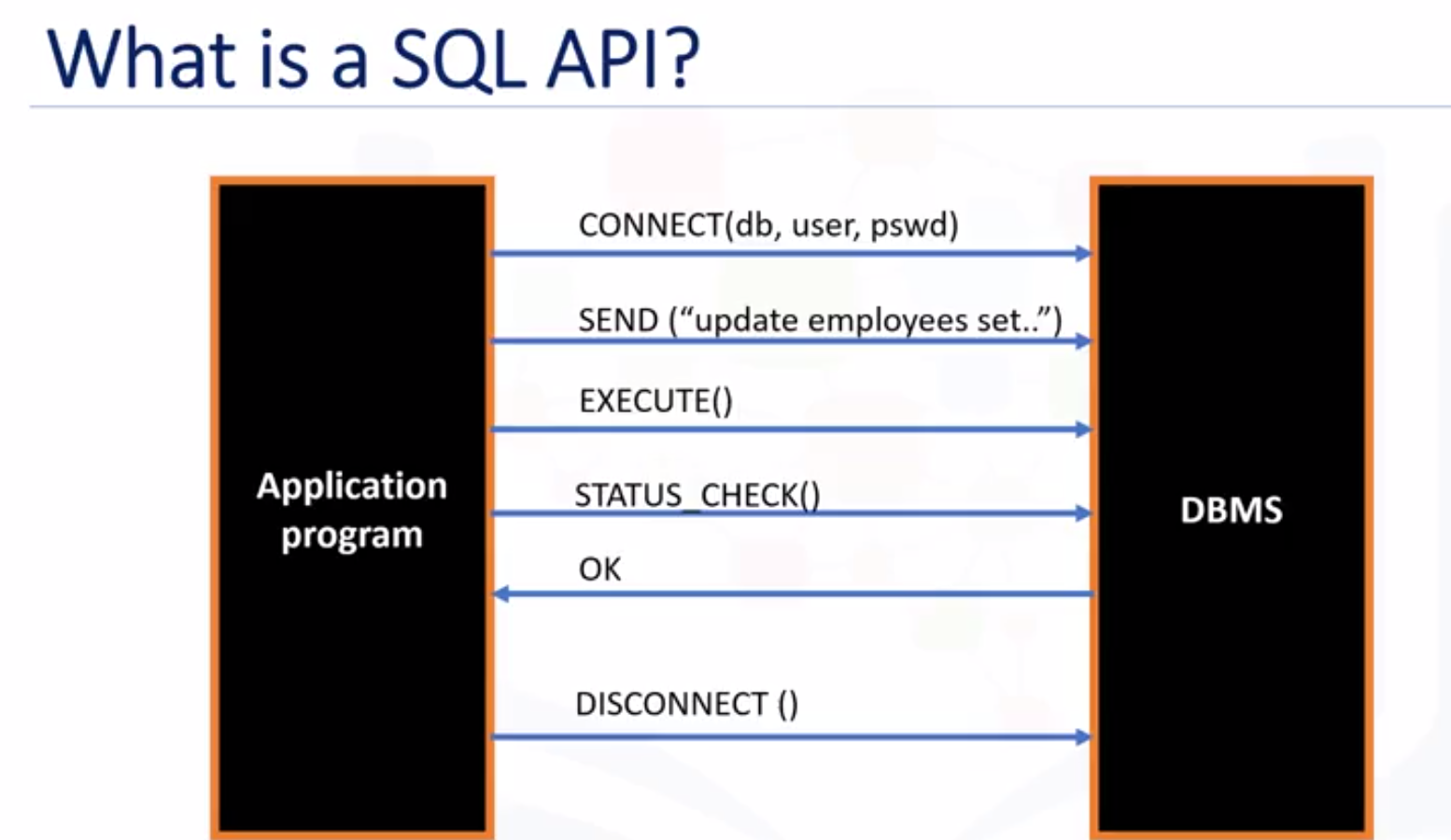
- Python connects to DBMS (database management system) using API codes: SQL APIs and Python DB APIs.
- The SQL API consists of library function calls as an application programming interface, API, for the DBMS. To pass SQL statements to the DBMS, an application program calls functions in the API, and it calls other functions to retrieve query results and status information from the DBMS.
Writing code using DB-API
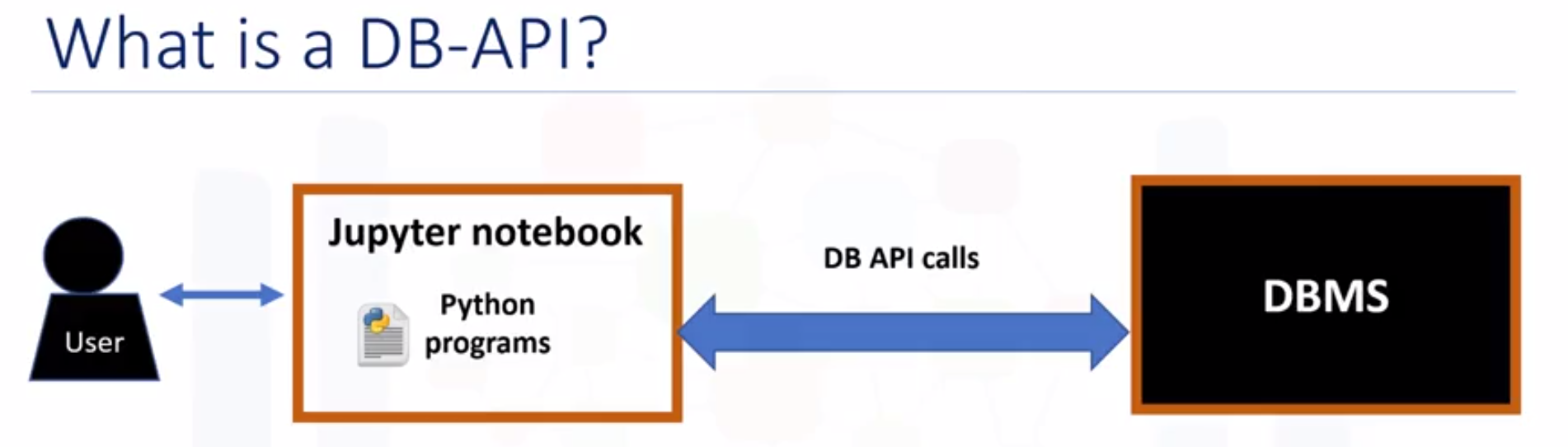
- Concepts of the Python DB API:
- Connection Objects: to connect to a database and manage your transactions.
- Database connections
- Manage transactions
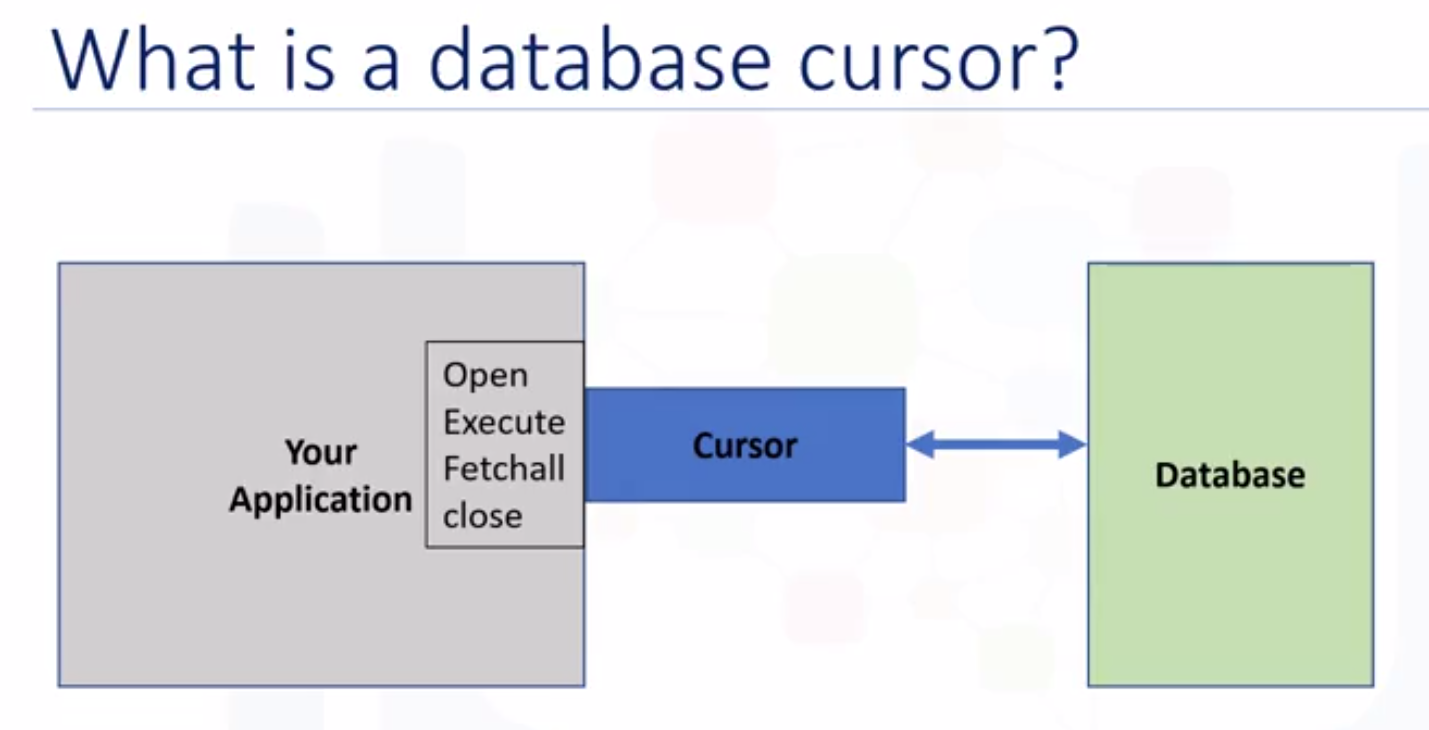
- Cursor objects: are used to run queries, are used to manage the content of a fetch operation.
- Database queries.
- A database cursor is like a file handle in that it enables you to scan through a result set of a query.
from dbmodule import connect # Create connection object Connection = connect('<databasename>', '<username>', '<password>') # Create a cursor object Cursor = connection.cursor() # Run Queries Cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM mytable') Results = cursor.fetchall() # Free resources Cursor.close() Connection.close() - Connection Objects: to connect to a database and manage your transactions.
- Remember that it is always important to close connections to avoid unused connections taking up resources.
Connecting to a database using ibm_db API
Working on Db2 Warehouse on Cloud Database:
- Try this notebook (need to sign in) or run the file /week3/DB0201EN-Week3-1-1-Connecting-v4-py.
- At first steps, you need to use your won create your own credentials, use file Week3/Wk3-LAB-0—v5—Create-Db2-Service-Credentials.pdf to create/use your credential.
- Note that
dsn_uidisusernamein the credential.
Below are the notes,
- Import ibm_db
import ibm_db - Identify database connection credenticals
dsn_driver = "IBM DB2 ODBC DRIVER" dsn_database = "BLUDB" dsn_hostname = "dashdb_entry_yp_da..." dsn_port = "50001" dsn_protocol = "TCPIP" dsn_uid = "dash****" dsn_pwd = "***********" - Create a database connection
# Create database connection dsn = ( "DRIVER = ...;" "DATABASE = {0};" "HOSTNAME = {1};" "PORT = {2};" "PROTOCOL = TCPIP;" "UID = {3};" "PWD = {4};").format(dsn_database, dsn_hostname, dsn_port, dsn_uid, dsn_pwd) try: conn = imb_db.connect(dsn, "", "") print("Connected!") execpt: print("Unable to connect to the databse") - Close the connection
ibm_db.close(conn) - Remember that it is always important to close connections so that we can avoid unused connections taking up resources.
Creating tables, loading data and querying data
Check the file Week3/DB0201EN-Week3-1-2-Querying-v4-py.ipynb for the lab.
- Connect to the IBM Db2 like the previous section.
- Use following syntax
stmt = ibm_db.exec_immediate(conn, "SQL statements" ) # how to fetch data ibm_db.fetch_both(stmt) - Using pandas
import pandas import ibm_db_dbi pconn = ibm_db_dbi.Connection(conn) df = pandas.read_sql('<SQL statements>', pconn) - Accessing databases with SQL magic
- Check file for more info & examples: week3/DB0201EN-Week3-1-3-SQLmagic-v3-py.ipynb
- “Magic” is JupyterLab’s term for special commands that start with “%”.
- You can use python variables in your SQL statements by adding a “:” prefix to your python variable names.
- You can use the normal python assignment syntax to assign the results of your queries to python variables.
-
Example of using/not using SQL magic (cf)
import pandas as pd from sqlalchemy.engine import create_engine # Presto engine = create_engine('presto://localhost:8080/system/runtime') #Read Presto Data query into a DataFrame df = pd.read_sql('select * from queries limit 1', engine) df.head()- if we use SQL magic
pd = %sql select * from runtime.queries limit 1 pd.DataFrame().head()
Analyzing data with Python
- Check the file week3/DB0201EN-Week3-1-4-Analyzing-v5-py.ipynb
OPTIONAL: Using JOIN operations to work with multiple tables
- Working with multiple tables
- W3School JOIN
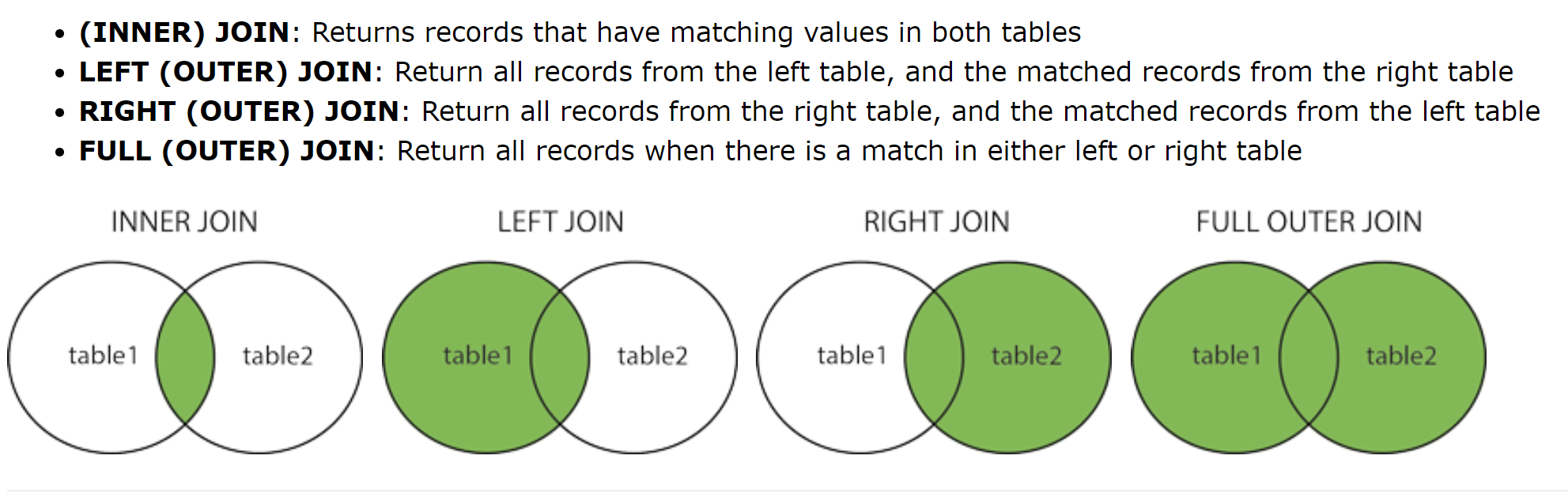
- Learn about Inner join, Left join, Right join, Full join, Self join
Week 4: Course Assignment
- In many cases data sets are made available as .CSV files which contain data values separated by commas.
- Sometimes the first row of the CSV file contains the name of the column.
select id from dogsleads to Error: “ID” is not valid in the context where it is used.. SQLCODE=-206, SQLSTATE=42703, DRIVER=4.22.36 because the database parser assumes uppercase names by default.- Use:
select "Id" from DOGS, note that we need to use double quotes"instead of'!
- Use:
- spaces, brackets, special characters may be mapped to underscore. Remember to use uderscore for these charaters in the column name.
- Using quotes in Jupyter notebook
selectQuery = 'select "Id" from dogs' selectQuery = 'select * from dogs where "Name_of_Dog"=\'Huggy\' ' - Splitting queries to multiple lines in notebooks
selectQuery = 'select "Id", "Name_of_Dog", \ "Breed__dominant_breed_if_not_pure_breed_" from dogs \ where "Name_of_Dog"=\'Huggy\'' - Restricting number of rows retrieved:
select * from census_data LIMIT 10 - To get a list of tables in a Db2 database you can run the following query:
select * from syscat.tables - Check file week4/DB0201EN-Week4-1-1-RealDataPractice-v4-py.ipynb for more info about working with Db2.
Problems
Problem 1. Find the total number of crimes recorded in the CRIME table
%sql SELECT COUNT(*) FROM CHICAGO_CRIME_DATA
Problem 2. Retrieve first 10 rows from the CRIME table
%sql SELECT * FROM CHICAGO_CRIME_DATA LIMIT 10
Problem 3. How many crimes involve an arrest?
%sql SELECT COUNT(*) FROM CHICAGO_CRIME_DATA WHERE ARREST=TRUE
Problem 4. Which unique types of crimes have been recorded at GAS STATION locations?
%sql SELECT DISTINCT PRIMARY_TYPE FROM CHICAGO_CRIME_DATA WHERE LOCATION_DESCRIPTION='GAS STATION'
Problem 5. In the CENUS_DATA table list all Community Areas whose names start with the letter ‘B’.
%sql SELECT * FROM CENSUS_DATA WHERE COMMUNITY_AREA_NAME LIKE 'B%'
Problem 6. Which schools in Community Areas 10 to 15 are healthy school certified?
%sql SELECT S.COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER, S.NAME_OF_SCHOOL, S.HEALTHY_SCHOOL_CERTIFIED FROM CHICAGO_PUBLIC_SCHOOLS S, CENSUS_DATA C \
WHERE S.COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER = C.COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER \
AND (C.COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER BETWEEN 10 AND 15) \
AND (S.HEALTHY_SCHOOL_CERTIFIED = 'Yes')
Problem 7. What is the average school Safety Score?
%sql SELECT AVG(SAFETY_SCORE) FROM CHICAGO_PUBLIC_SCHOOLS
Problem 8. List the top 5 Community Areas by average College Enrollment [number of students]
%sql SELECT C.COMMUNITY_AREA_NAME, N.AVG_COLLEGE_ENROLLMENT \
FROM CENSUS_DATA C, (SELECT COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER, AVG(COLLEGE_ENROLLMENT) \
AS AVG_COLLEGE_ENROLLMENT \
FROM CHICAGO_PUBLIC_SCHOOLS \
GROUP BY COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER) N \
WHERE C.COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER = N.COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER \
ORDER BY N.AVG_COLLEGE_ENROLLMENT DESC LIMIT 5
Problem 9. Use a sub-query to determine which Community Area has the least value for school Safety Score?
%sql SELECT COMMUNITY_AREA_NAME FROM CENSUS_DATA WHERE COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER = \
(SELECT COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER FROM CHICAGO_PUBLIC_SCHOOLS WHERE SAFETY_SCORE = \
(SELECT MIN(SAFETY_SCORE) FROM CHICAGO_PUBLIC_SCHOOLS))
Problem 10. [Without using an explicit JOIN operator] Find the Per Capita Income of the Community Area which has a school Safety Score of 1.
%sql SELECT PER_CAPITA_INCOME FROM CENSUS_DATA WHERE COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER = \
(SELECT COMMUNITY_AREA_NUMBER FROM CHICAGO_PUBLIC_SCHOOLS WHERE SAFETY_SCORE=1)
